Digital tools empower architects to step out of the box and deliver unique structures. They’re also helping them reduce building costs while maintaining efficiency and sustainability goals.
Architects are responsible for ensuring their designs are visually appealing and use environmentally friendly materials. Achieving the perfect balance between these two aspects is crucial in creating sustainable and beautiful buildings. AI can help them achieve this by analyzing and optimizing material use and energy performance.
Visualization
Visualization is the process of creating images to communicate information. It has been used since the invention of the central perspective in the Renaissance and continues to be an essential tool for communicating abstract and concrete ideas.
Architect Gladwyne uses visualization to help them reach their goals. It helps you focus on what matters most and creates motivation for action.
3D Printing
Often associated with maker culture and hobbyists, 3D Printing is now widely available thanks to affordable desktop printers. It prints parts on demand using polymer plastics like PLA or crunchable polylactic acid, photopolymers, epoxy resins, and metals.
First, a virtual design is made using CAD software, and then the model is printed in layers. It means less wasted inventory and faster production.
3D Scanning
3D scanning, or reality capture, transforms objects in the real world into digital models. These models can be used for a wide range of applications.
Choose a plain, non-reflective surface for your object to ensure the scan is accurate. Avoid transparent or dark surfaces as they confuse the depth sensors of the scanner and create reflections that cannot be captured.
Photogrammetry uses photos to reconstruct a 3D model of an object. Laser triangulation and structured light are other popular methods of 3D scanning.
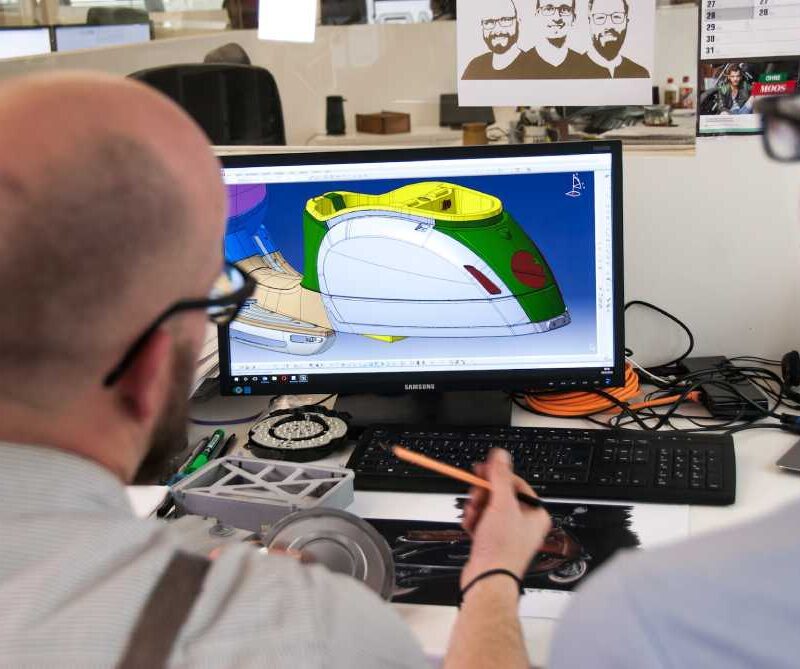
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Computer-aided design is an ingenious digital technology that acts like a design chameleon. These 2D and 3D models are digital doodles and sophisticated data repositories that permit millimeter-precise measurements, swift alterations, and simulations.
Many federal agencies use CAD to design various tools, equipment, and buildings.
Virtual Design and Construction
Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) is a holistic process that uses detailed 3D models to plan and manage projects. It cultivates more effective communication and collaboration between architects, engineers, and contractors and helps reduce project costs by minimizing the need for costly corrections during construction.
This study tests two distinct VR methods: a gamification-based platform using Unreal Engine and a BIM method using the Enscape plugin for Revit as co-design approaches in architecture and urban design. The results indicate that both systems can improve visualization, enhance communication, and streamline decision-making.
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
This technology allows architects, engineers, and construction teams to collaborate in a three-dimensional virtual design environment. Its information-sharing capabilities help reduce project errors and costly delays, including change orders.
Moreover, BIM models can be used for fabrication, shop drawings, code reviews, cost estimating, and construction sequencing. However, the process can be complicated and requires extensive training.
The advanced BIM process allows design and construction teams to share information through a common database. It facilitates coordination and reduces risk by anticipating clash detection early in the process.
Surveys have shown that BIM saves time and money for participants in the construction process, including architects, engineers, project managers, and contractors. However, some needs to be clarified about adequately implementing and using BIM.
BIM processes use database-first modeling software to enable teams to work together on the planning, design, construction, and maintenance of a building. It allows the design team to coordinate the construction process better and detect clashes between equipment, MEP, and internal systems – eliminating expensive rework that could result in construction delays.
BIM also helps create a better-coordinated specification for the project, using structured templates to ensure accuracy. This information can be used by those who will operate the building in the future to plan and execute operations and maintenance.
It allows everyone involved in a construction project to virtually navigate through and experience a space before construction, reducing preconstruction clashes and eliminating construction schedule setbacks. It can also improve knowledge transfer from office to field, reducing change orders and field coordination problems.
It utilizes database-first technology and replaces graphics-first design software, allowing all stakeholders to edit a single dataset. The model can also be used for building operations and maintenance later on.